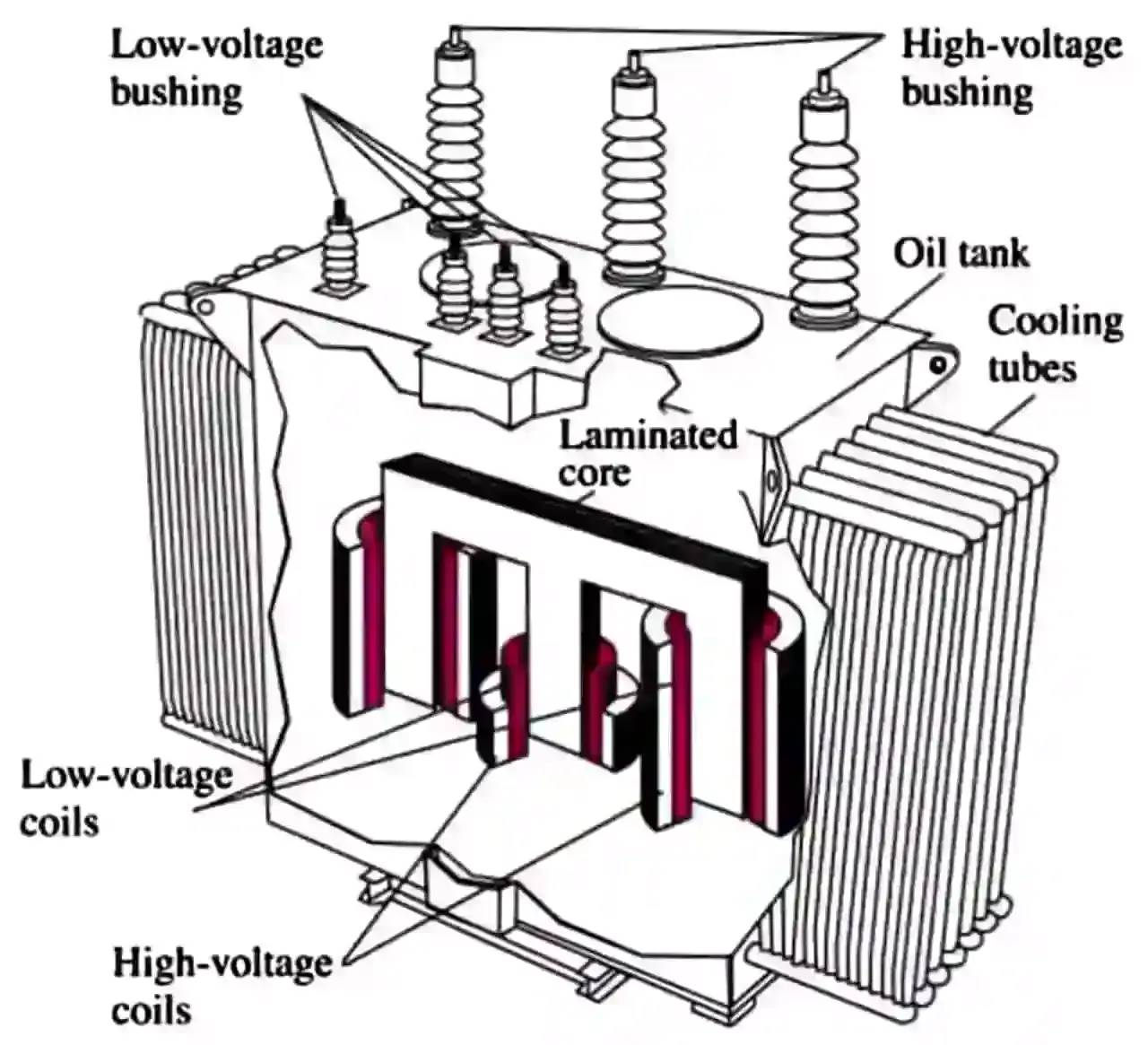
This is because oil-immersed transformers contain transformer oil, which serves as both the insulation material for the transformer core and coils and as the heat transfer medium.
The heat generated by the operating transformer core and coils is dissipated through the flow of transformer oil and the cooling fins of the transformer casing, ensuring the safe operation of oil-immersed transformers. Additionally, to prevent oil leakage, the protective rating of the transformer casing is relatively high, making it resistant to outdoor exposure.

Dry-type transformers, on the other hand, typically use epoxy resin insulation, which tightly encapsulates the transformer core and coils, resulting in poorer heat dissipation performance.
Even if dry-type transformers have casings, their protective rating cannot be too high, hence they are generally safer for indoor installation.